Orthognathic Surgery, Jaw Misalignment, Jaw Pain, Orthodontic Treatment.
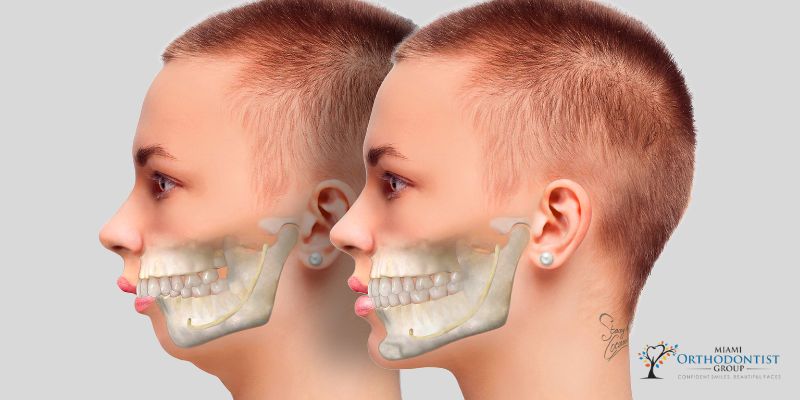
Jaw misalignment, or malocclusion, can lead to many issues, ranging from difficulties in chewing and speaking to facial asymmetry and even breathing problems.
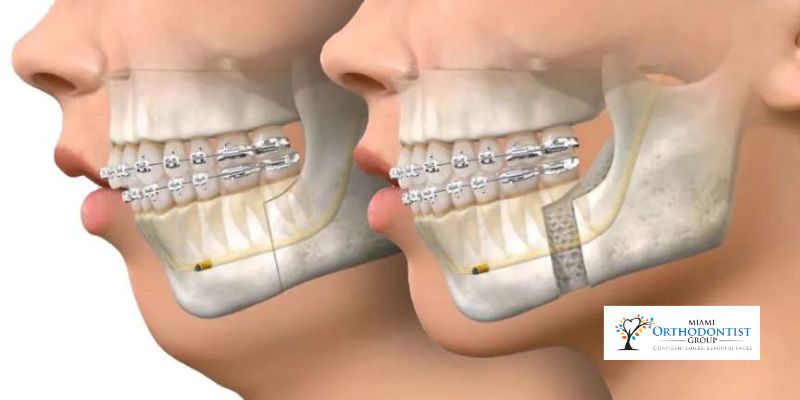
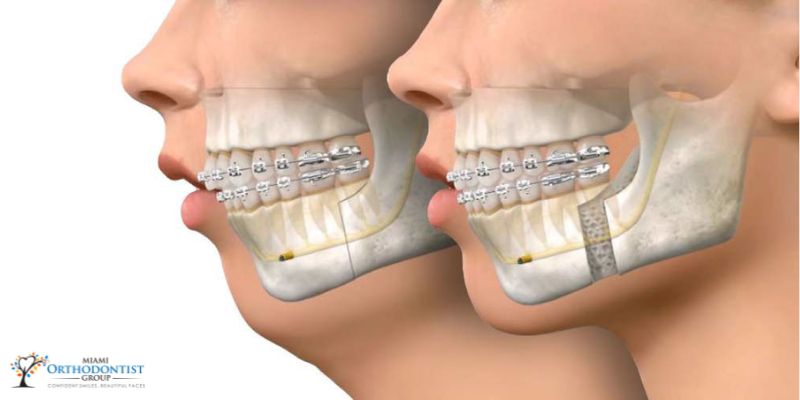
Orthognathic surgery, a transformative intervention in oral and maxillofacial surgery, is pivotal in enhancing oral health by addressing a spectrum of bite issues.
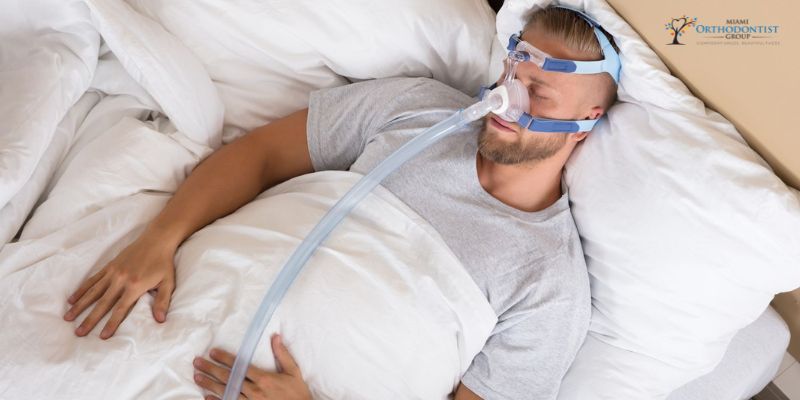
Millions of people worldwide suffer from the common sleep disease known as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It is caused by the obstruction or narrowing of the upper airway, which results in snoring and irregular breathing while you sleep. OSA can harm health, including a higher risk of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Orthognathic surgery, which …
Continue reading "How Can Orthognathic Surgery Treat Sleep Apnea?"
Did you know that 20% of people have severe facial growth deformities to a higher degree? You might find this alarming at first. A substantial facial defect isn't always as easy as people may assume.
Are you aware of Orthognathic Surgery In Miami? Orthognathic surgery is done to adjust the misalignment of jaws and teeth that cannot be cured with orthodontic treatment. The process intends to fix and shift extreme abnormalities among the upper and lower jaws, which allow the teeth to bite together properly.
Orthodontic Surgery and Treatment is often shrouded in mystery. There is a lot of information involved as well as many variables at play. In such a field where information is plenty and professionals are few, it’s easy to get many misinformed opinions thus the myths.
Dental emergencies can happen to anyone at any time. It can happen when you are awake, when you are sleeping, when you are doing exercise, when you are taking, and when you are eating. It could cause a lot of pain, discomfort, and bleeding.