What exactly is an overbite?
When the upper teeth are 30 to 50% larger than the lower teeth, it is called overbite or overbite. Malocclusion is the medical term for this problem. Sometimes an overbite appears to be a problem with a person’s teeth, but in reality, it’s that person’s teeth and jaws are not aligned properly. Overbites can run in families, as some people are born with abnormally shaped breasts that develop unevenly as they grow.
Types of overbite:
Vertical overbite is when a person’s upper teeth significantly overlap the lower teeth.
Horizontal overbite occurs when the upper teeth overbite the lower teeth.
Whether an overbite is classified as vertical or horizontal, some patients present with both symptoms at the same time. Overbites can also be classified as skeletal or dental in nature. A dental overbite means that the teeth are responsible for creating the overbite. In the case of a skeletal overbite, the jaw is the cause of the overbite.
What factors contribute to the development of overbite?
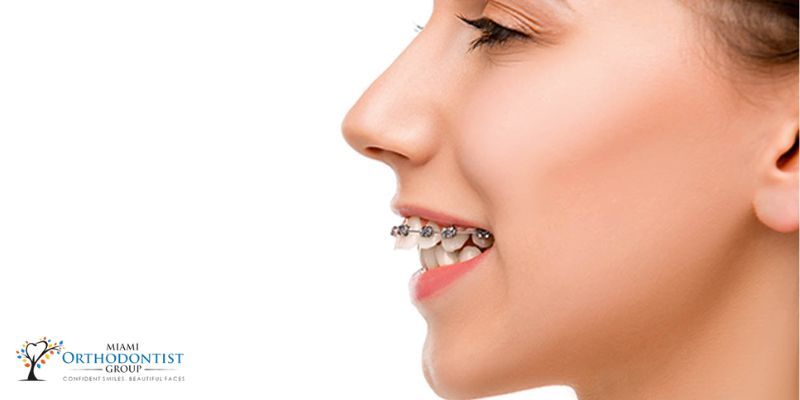 Overbite is often caused by the shape and/or size of the teeth or jaw. This can mean that there is too much or too little space in the mouth to accommodate the size of the teeth. If left untreated, an overbite will manifest itself as teeth clattering and chattering if there are not enough space, or teeth that are too far apart if the bite is too large.
Overbite is often caused by the shape and/or size of the teeth or jaw. This can mean that there is too much or too little space in the mouth to accommodate the size of the teeth. If left untreated, an overbite will manifest itself as teeth clattering and chattering if there are not enough space, or teeth that are too far apart if the bite is too large.
In infants and children, habits such as thumb sucking, constant cupping, and excessive bottle drinking – all of which cause the back teeth – can lead to an overbite. This can cause exclusions in teenagers and adults who are used to raising their eyebrows and using writing utensils such as eyebrow pencils or other objects. Similarly, tooth loss without timely repair can lead to exclusion. According to recent studies, nearly three-quarters of children show signs of exclusion.
What if I do not treat it ?
If she is not treated, supraclusion can lead to serious health issues. These include irreversible damage to the teeth as a result of an abnormal posture and probable neck pain, including problems with the temporo-mandibular joint (ATM).
Additional side effects of supraclusion include:
- Discomfort or pain when eating
- Tooth decay, including gum disease and tooth enamel wear
- Severe headaches
- Jaw pain
- Difficulty speaking
- Difficulty opening or closing the mouth completely,
- Sleep apnea
In addition to changing the shape of the face, an untreated overbite can also lead to psychological problems such as low self-esteem. Teenagers with overbite may experience social problems, such as being tormented by their peers. They may be bullied throughout their adult lives.
Overbite treatment
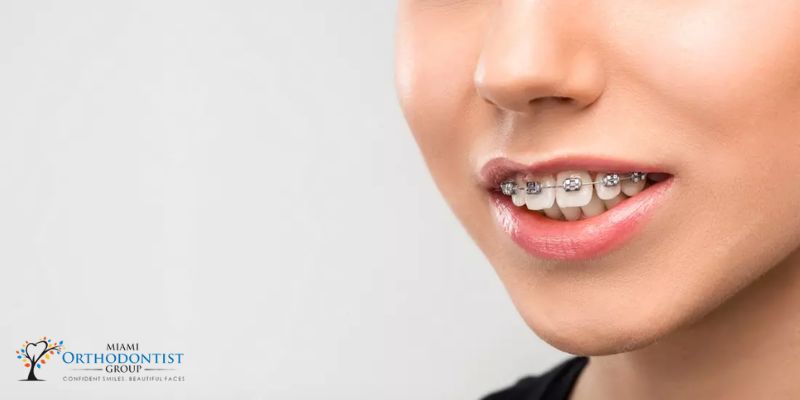 The gravity of the malocclusions previously mentioned dictates the need for treatment. Medically speaking, a shift of 2 to 4 millimeters typically does not necessitate a correction. However, some patients may already desire a treatment based on aesthetic and cosmetic considerations. In order to avoid the above-mentioned preclusion issues, orthodontic treatment should be considered if the anterior vertical or horizontal overbites exceed 4 millimeters.
The gravity of the malocclusions previously mentioned dictates the need for treatment. Medically speaking, a shift of 2 to 4 millimeters typically does not necessitate a correction. However, some patients may already desire a treatment based on aesthetic and cosmetic considerations. In order to avoid the above-mentioned preclusion issues, orthodontic treatment should be considered if the anterior vertical or horizontal overbites exceed 4 millimeters.
Braces are the most common method of correcting an overbite. However, if you prefer not to have visible brackets and wires in your mouth, you can turn to the contemporary method of therapy. This involves using barely visible plastic trays that put pressure on the teeth and move them into the desired position. With a conventional dental X-ray machine, this process can take up to two years or more. With the best mile trays, in just three to twelve months, your teeth will be in great shape.
Repositioning the teeth and jaws is essential in some cases, while surgery is required in others. This may be the case if the teeth are moved by more than 9 millimeters. If you have an overbite, our dentists will work with you one-on-one and explain the various treatment options available.
Summary
If your supraclusion is causing you problems, make an appointment with an orthodontist or a dentist who specializes in oral surgery. The best way to avoid dental problems in children and adults alike is to schedule regular checkups. For the direction of a supraclusion, dentists recommend a checkup for children as young as seven years old. Adults must submit to regular checks every six to ten months in order to ensure early management and avoid the potentially heavy physical consequences of untreated supraclusion.


