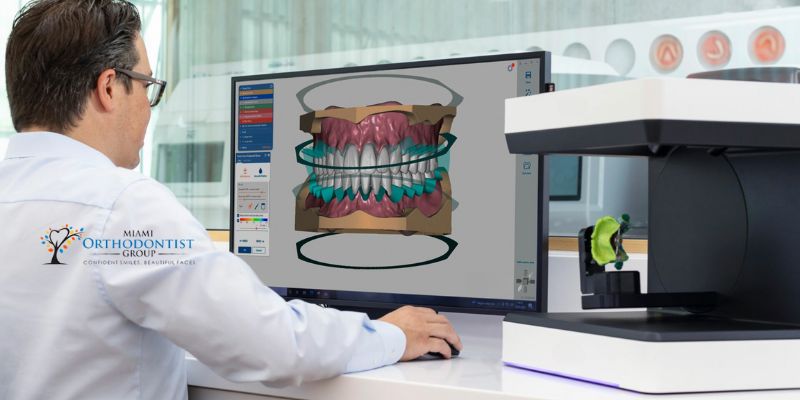
In recent years, 3D printing technology has revolutionized various industries and dentistry is no exception. Traditional dental techniques often require labor-intensive processes and the involvement of multiple professionals. However, a remarkable transformation has occurred with the advent of 3D printing in modern dentistry.
This technology has significantly enhanced dental procedures’ efficiency, precision, and customization, leading to improved patient outcomes and a more seamless dental experience. In this article, we will explore the various applications of 3D printing in modern dentistry and how it has revolutionized the field.
3D Printing Applications in Modern Dentistry
1. Customized Dental Prosthetics
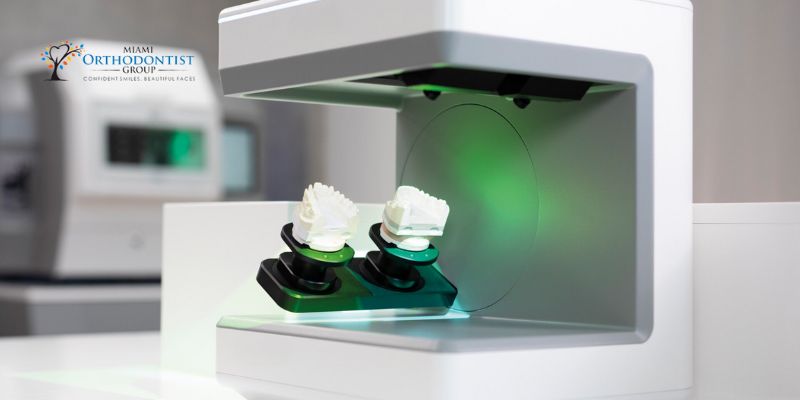

One of the most significant applications of 3D printing in modern dentistry is the creation of customized dental prosthetics. Whether it’s dental crowns, bridges, or dentures, 3D printing allows for the precise fabrication of prosthetics tailored to each patient’s unique dental anatomy.
Digital intraoral scanners capture detailed 3D images of the patient’s teeth, which are then used to create accurate digital models. These models can be easily modified and adjusted to ensure a perfect fit before sending them to the 3D printer for fabrication. As a result, patients experience improved comfort, aesthetics, and function compared to traditional prosthetics.
2. Surgical Guides and Implants
3D printing has revolutionized the process of dental implant placement by enabling the creation of surgical guides. These guides are generated based on a patient’s CT scan data, providing dentists with a preoperative visualization of the surgical site.
The surgical guides act as a roadmap during implant placement, enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of complications. With 3D printing, dental professionals can fabricate patient-specific implants with complex geometries that fit precisely into the patient’s unique bone structure. This level of customization not only ensures better integration of the implant but also accelerates the overall treatment process.
3. Orthodontic Aligners and Braces
Orthodontics has seen a significant transformation with the application of 3D printing technology. Instead of traditional braces, patients can now opt for clear aligners, such as Invisalign, which are custom-made using 3D printing.
After creating digital models of the patient’s teeth, the software generates a series of aligners that progressively move the teeth into their desired positions. The aligners are then 3D printed, allowing for a comfortable and virtually invisible treatment option. Moreover, 3D printing enables the production of orthodontic appliances like retainers and space maintainers, further expanding patient treatment options.
4. Dental Education and Training
3D printing has proven to be a valuable tool in dental education and training. Dental students and practitioners can use 3D-printed anatomical models to practice dental procedures, such as tooth extraction, root canal treatment, and implant placement.
These models offer a realistic representation of human dental anatomy, allowing students to gain practical experience without needing human subjects. Additionally, 3D-printed models can demonstrate complex dental cases to patients, helping them better understand their treatment plans and potential outcomes.
5. Prosthetic Restorations for Maxillofacial Reconstruction
Patients who have suffered from facial trauma or congenital deformities often require complex maxillofacial reconstruction. 3D printing plays a vital role in these cases, enabling the creation of custom prosthetics such as facial implants and prosthetic ears, noses, and other facial features.
These prosthetics are designed based on precise 3D scans of the patient’s facial structure, ensuring a seamless fit and natural appearance. 3D printing in maxillofacial reconstruction improves aesthetics, helps restore vital functions, and improves the patient’s overall quality of life.
6. Digital Workflow and Efficiency
Incorporating 3D printing into modern dentistry has streamlined the treatment workflow, increasing efficiency and reducing turnaround times. The need for traditional physical impressions has diminished with the digitization of dental processes, including scanning, designing, and 3D printing.
This eliminates the discomfort associated with traditional impression materials and expedites the treatment. Digital files can be easily shared between dental professionals, laboratories, and specialists, facilitating collaboration and communication to provide patients with the best possible care.
7. Cost-Effectiveness and Waste Reduction
Although 3D printing technology involves initial investment costs, it can ultimately lead to significant cost savings in the long run. The ability to create dental prosthetics and appliances with precision reduces the need for multiple adjustments and remakes, saving both time and resources.
Additionally, 3D printing allows dental laboratories to optimize material usage, minimizing waste and lowering material costs. As technology advances, the cost of 3D printing equipment becomes more accessible to smaller dental practices, making it a viable option for dentists across various settings.
8. Dental Restorations for Children
3D printing has proven particularly beneficial in pediatric dentistry, where children may require specialized dental restorations. Traditional dental procedures can be daunting for young patients, but 3D printing technology offers a less intimidating and more child-friendly approach.
Custom-made dental crowns and other restorations can be designed to resemble children’s favorite characters or colors, helping to alleviate their anxiety and make dental visits more enjoyable.
Moreover, 3D printing facilitates the creation of space maintainers and orthodontic appliances, addressing oral issues in children early on and promoting better oral health throughout their lives.
9. Advancements in Dental Materials
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, there have been significant advancements in dental materials compatible with 3D printers. Dental resins and ceramics specifically developed for 3D printing offer enhanced strength, durability, and aesthetics.
These materials have been extensively tested and approved for dental use, ensuring their safety and reliability. As new materials are continually developed, the possibilities for 3D printing in dentistry continue to expand, enabling even more innovative and specialized applications.
Conclusion
The application of 3D printing in modern dentistry has ushered in a new era of personalized and precise patient care. This technology has revolutionized dentistry, from customized dental prosthetics to orthodontic aligners and maxillofacial restorations to improved treatment outcomes and patient experiences. As 3D printing continues to evolve and become more accessible, its potential to further transform dental practice and advance patient care is fascinating.